:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/processus-mastoideus/i69qkAHvcUSvEuXXQsZVTQ_Mastoid_process_01.png)
Petrous Portion Of Temporal Bone slidesharedocs
Petrous part of the temporal bone on a CT Scan: normal anatomy. We have created an atlas of the temporal bone which is an educational tool for studying the normal anatomy of the petrous bone based on an MDCT exam of the axial and coronal of the ear and petrous bone. Anatomical structures are visible as interactive labeled images.
Os temporale Axon
Het rotsbeen, steenbeen, os petrosum of pars petrosa ossis temporalis is een onderdeel van het slaapbeen (os temporale) van de schedel.Het bevindt zich zowel links als rechts aan de binnenkant van de schedel. De margo superior van het rotsbeen geeft de scheiding aan tussen de achterste schedelgroeve (fossa cranii posterior) en de middelste schedelgroeve (fossa cranii media).

耳的应用解剖学之颞骨的解剖结构 知乎
Inner and middle ear abnormalities (os petrosum) have been studied extensively in humans and mice because of their effect on hearing. Therefore, most anatomic anomalies seen in Chd7‐deficient mice had already been extensively documented in individuals with CHARGE syndrome.
Os temporale Axon
Temporal bone fracture is usually a sequela of significant blunt head injury. In addition to potential damage to hearing and the facial nerve, associated intracranial injuries, such as extra-axial hemorrhage, diffuse axonal injury and cerebral contusions are common. Early identification of temporal bone trauma is essential to managing the.
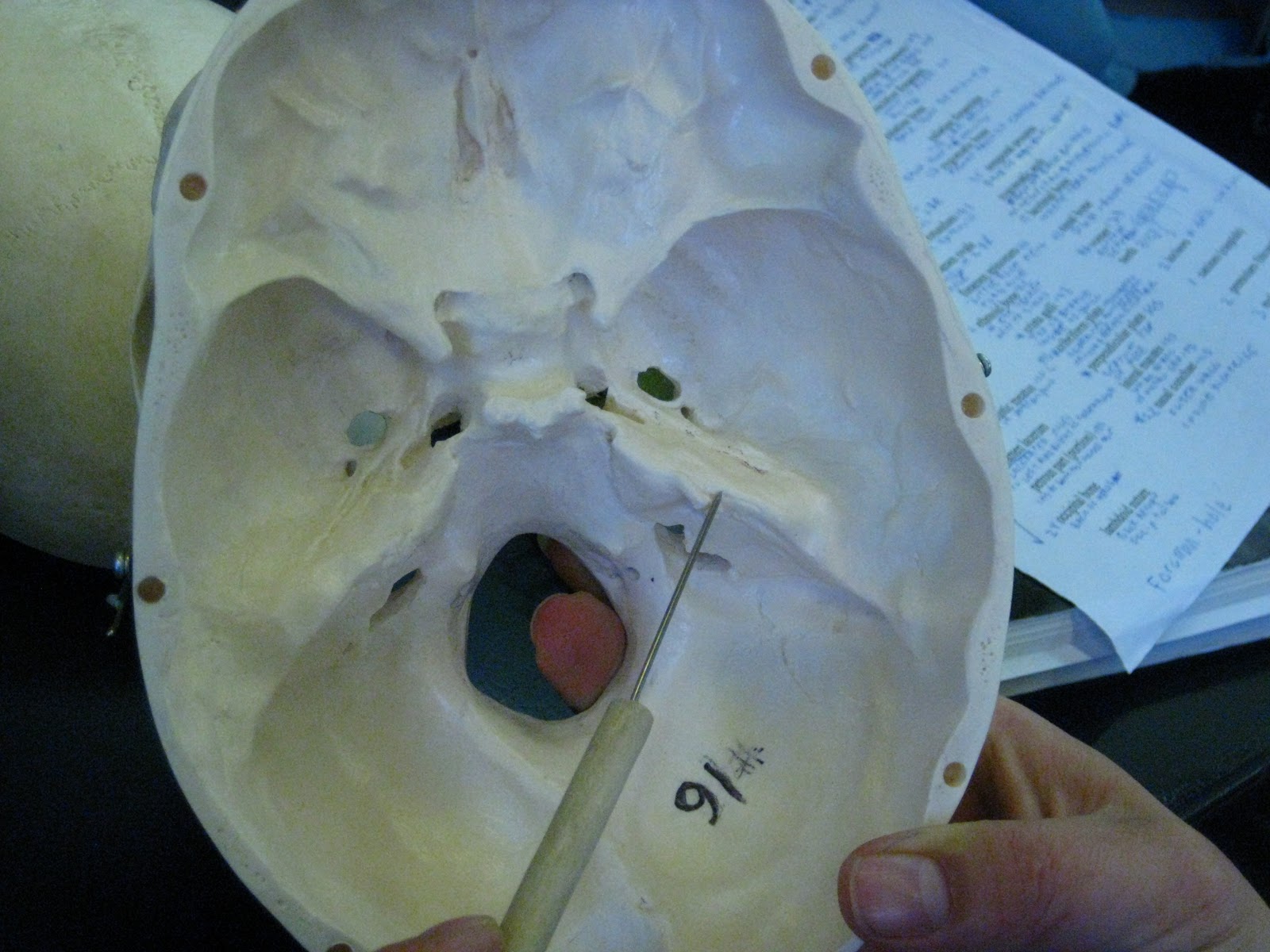
Boned Human Skull petrous part (of temporal bone)
Publicationdate 2016-01-15. This is an updated version of the 2007 article. In this review we present the normal axial and coronal anatomy of the temporal bone by scrolling through the images. Some structures are discussed in more detail with emphasis on related pathology. You will find more temporal bone pathology here.

Os petrosum (equus) Aspectus externa et interna YouTube
A 53-year-old male patient, with the diagnosis of CG since 2003 with slow progression, presented with diplopia and headache for a couple of weeks. MRI showed a 2.2 × 1.4 cm lesion in the transversal plane above the apex of the right os petrosum. The lesion appeared with a high intensity signal on both T 1 and T 2-weighted imaging.

The petrous part of the temporal bone (or more simply petrous temporal
Abstract. The anatomy of the petrous apex is described, a system for classifying petrous apex lesions is presented, and commonly encountered petrous apex lesions are discussed, with emphasis on clinical features, CT and MR imaging findings, and normal anatomic variants that may mimic disease. The petrous apex is a complex region of the central.

petrous temporal bone
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. There is a wide differential diagnosis of petrous apex lesions: pseudolesions. asymmetrical marrow / asymmetrical pneumatization. non-expansile. fat signal intensity on all sequences. petrous apex effusion 7. petrous apex cephalocele 4. CSF signal intensity on all sequences.

CTos petrosum
Attention is called to a little known cranial ossicle, the os supra petrosum (O.S.P.), located within the dura at the tip of the petrous bone. It is an anatomic variant which may be seen quite clearly in the roentgenograms. It is of no apparent clinical significance but should be recognized in the differential diagnosis of intracranial calcifications. Five children with this roentgen finding.

From Wikiwand Petrous part of the temporal Bones, Sphenoid bone
The non-pneumatized petrous apex will show fatty marrow appearing hyperintense on routine T1- and T2-weighted sequences with no expansion of the bone. Confirmation is made by observing the complete loss of signal with fat-saturation sequences. Asymmetric fatty infiltration of the apex may be observed as a conspicuous asymmetric high signal on.
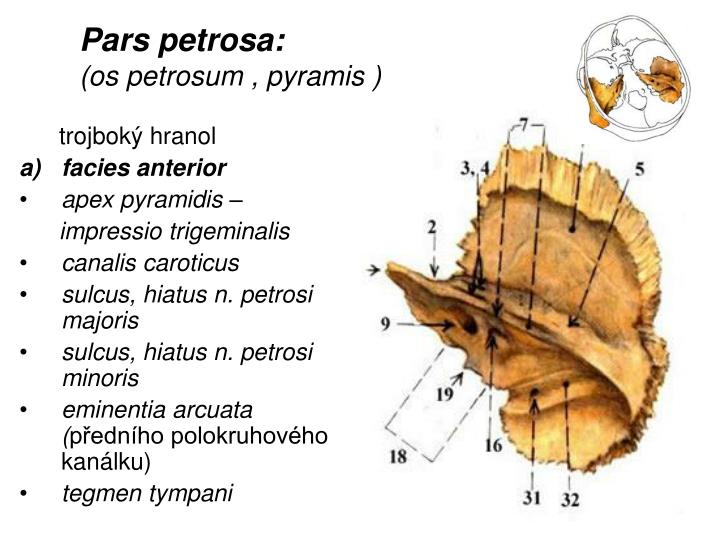
PPT Obecná nauka o kostech PowerPoint Presentation ID5090588
Case Discussion. Normal CT of the petrous temporal bones. The inner ear structures, ossicles and facial nerves are well demonstrated.

petrous temporal bone anatomy Ilustración de calaveras, Craneo
Figure 3. A 48-year-old female with a left-sided intraosseous schwannoma of the petrous apex measuring 8.5 mm in the anteroposterior, 7 mm in the transverse, and 7 mm in the craniocaudal dimensions. Axial T1W high resolution fat saturation MRI of the brain pre (3a, 3c) and post (3b, 3d) gadolinium administration at the level of the petrous apex.
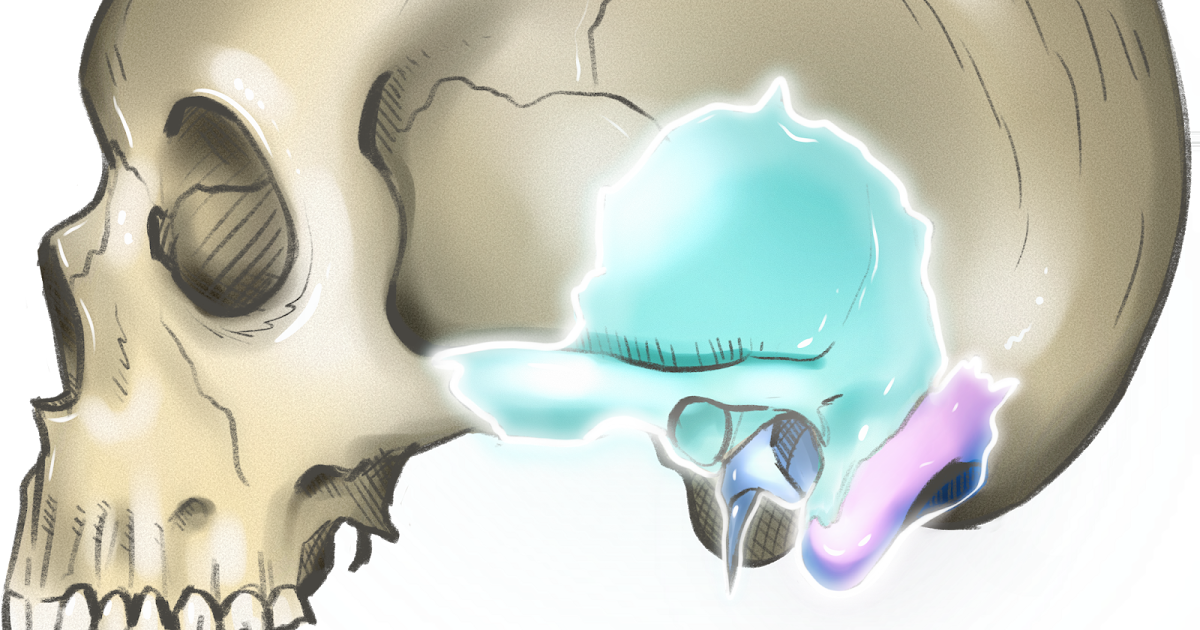
Os temporale Axon
The ossupra petrosum (O.S.P.) isde-scribed asasmall ossicle, pea-sized atthe most, located on the anterosuperior sur-face ofthe petrous bone, near the tip of this bone andjust anterior and medial to the ganglion ofGasser. Itlies under the dura either independent from itor ad-herent toit. It isusually bilateral and symmetrical and has apparently.
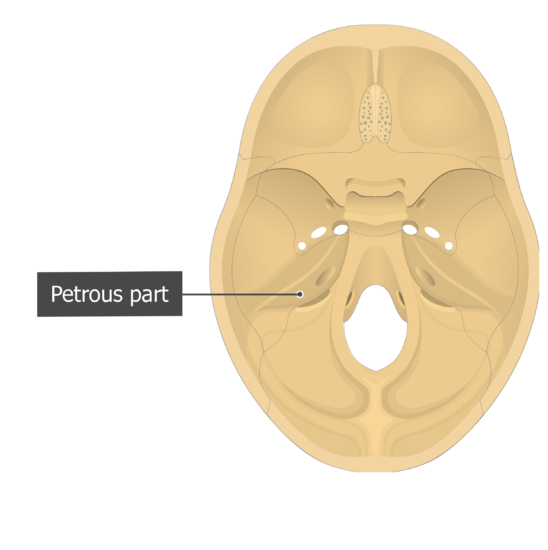
Temporal bone anatomy and labeled diagram GetBodySmart
Objective. The petrous apex is a pyramidal shaped, variably pneumatized structure of the skull base that forms a unique intersection between the suprahyoid neck and the intracranial compartment. Given its location, the petrous apex is susceptible to multiple pathologic processes including intrinsic lesions of bone, pneumatized air cells, or the.
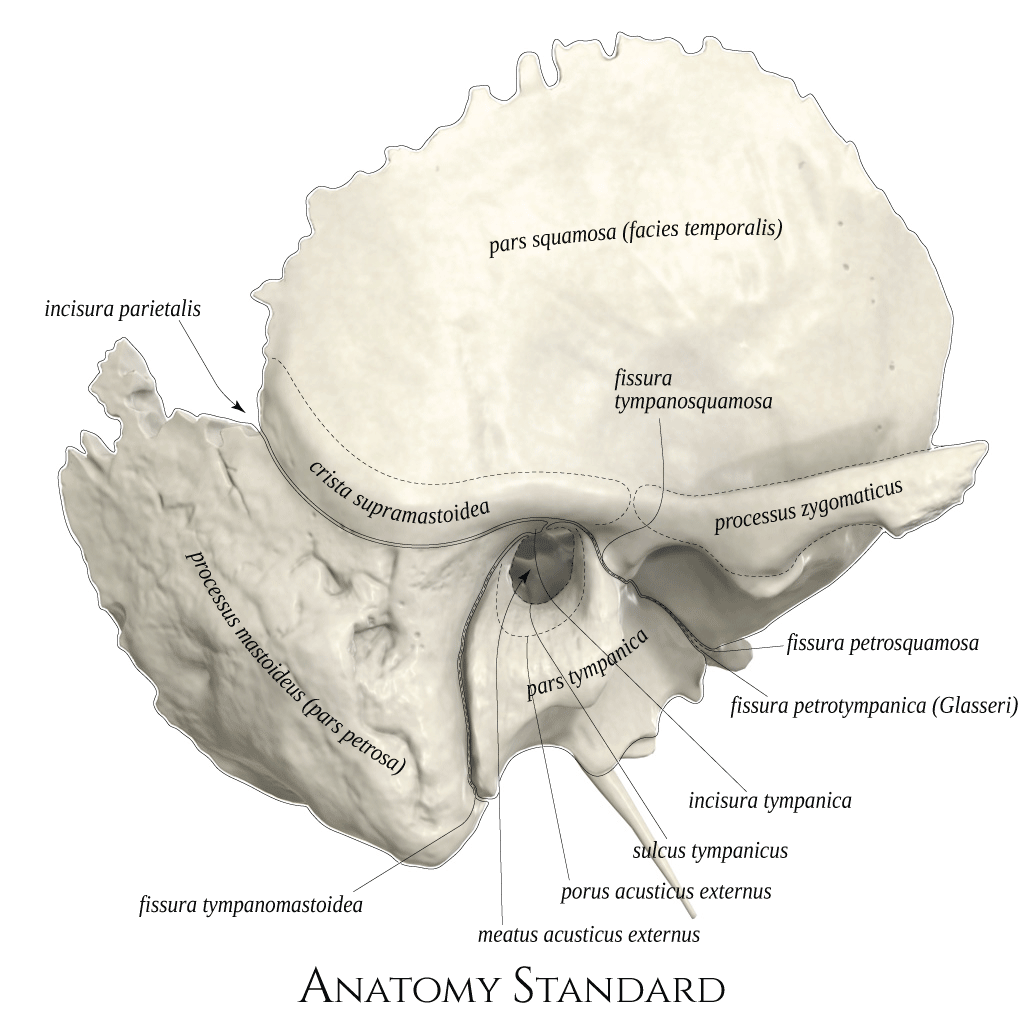
Anatomy Standard Drawing Temporal bone lateral view Latin labels
The rock bone (pyramid) is sometimes referred to separately as the bone of the os petrosum. It is a formation similar to a quadrilateral pyramid that protrudes laterally from the back in the ventromedial direction. It contains a complicated cavity space, the so-called labyrinthus osseus (bony labyrinth), in which the sensory organs of hearing.
The surface landmarks on the inferior surface of the petrous portion
Pneumatization of the petrous temporal bone apices is an anatomical variant that may be bilateral or asymmetrical. It is important not to confuse it with a pathological lesion especially on MRI. Benign lesions such as cholesterol granuloma and cholesteatoma are more likely to occur in a pneumatized petrous apex. Also, it can be a site for CSF.