
Tension in the cable of an elevatorformulaproblems DewWool
Michel van Biezen 972K subscribers 410 54K views 10 years ago PHYSICS 17 TENSION AND WEIGHT Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will show your how.

Weight of Scale on an Elevator (Physics Problem) YouTube
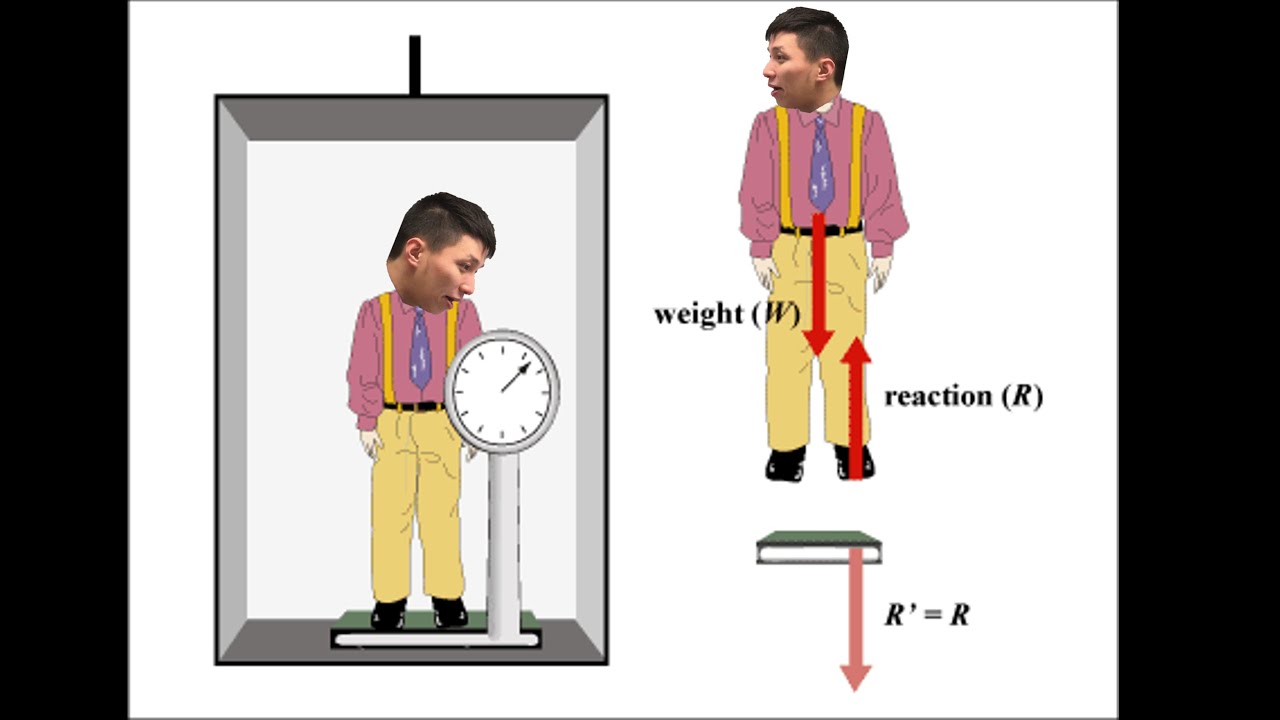
Spread the love. The elevator's free-body diagram has three forces, the force of gravity, a downward normal force from you, and an upward force from the tension in the cable holding the elevator. The combined system of you + elevator has two forces, a combined force of gravity and the tension in the cable. Table of Contents show.
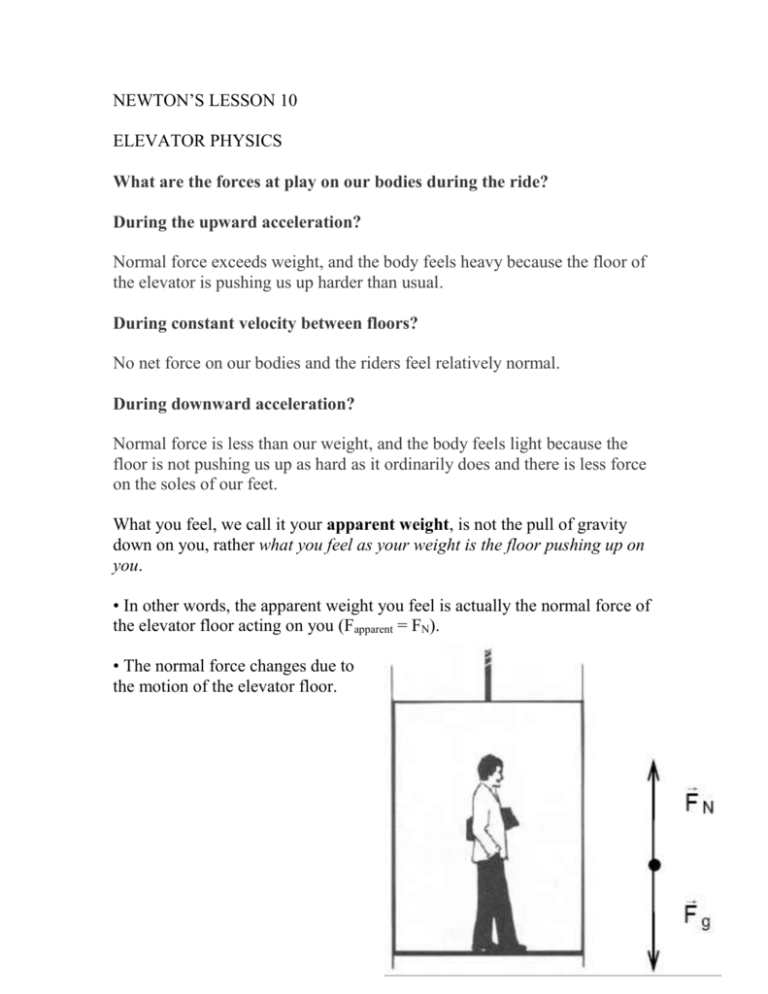
ELEVATOR PROBLEMS AND LAB
The "Elevator Problem" is a classic problem in physics. The situation is this: "You are standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator. You are holding an apple. (Yes, people staring at you.) You weigh 500 Newtons, so your mass is about 50 kg." This assignment is a step-by-step analysis of the elevator problem.
Elevator Problem (Classic!) IB Physics Chapter 2.2 (Part 7) YouTube
Normal Reaction in an Elevator in different situations [Elevator problems in Physics] Say a person is standing in an Elevator. his weight is acting downwards towards the floor of the elevator. The elevator surface in turn is applying a Reaction force. Let's start with our case studies from here, with this understanding.

13.2 Physics Displacement and distance covered in an accelerating elevator (Bolt Elevator
Elevators Problems: Problem (1): An student weighing 550 N stands on a spring scale in a 950-kg elevator (including the person). Just as the elevator starts moving, the scale reads the student's weight as 517 N. (a) What is the magnitude and direction of the elevator's acceleration? (b) Find the acceleration if the scale reads 572 N?

Elevator Physics Problem Normal Force on a Scale & Apparent Weight YouTube
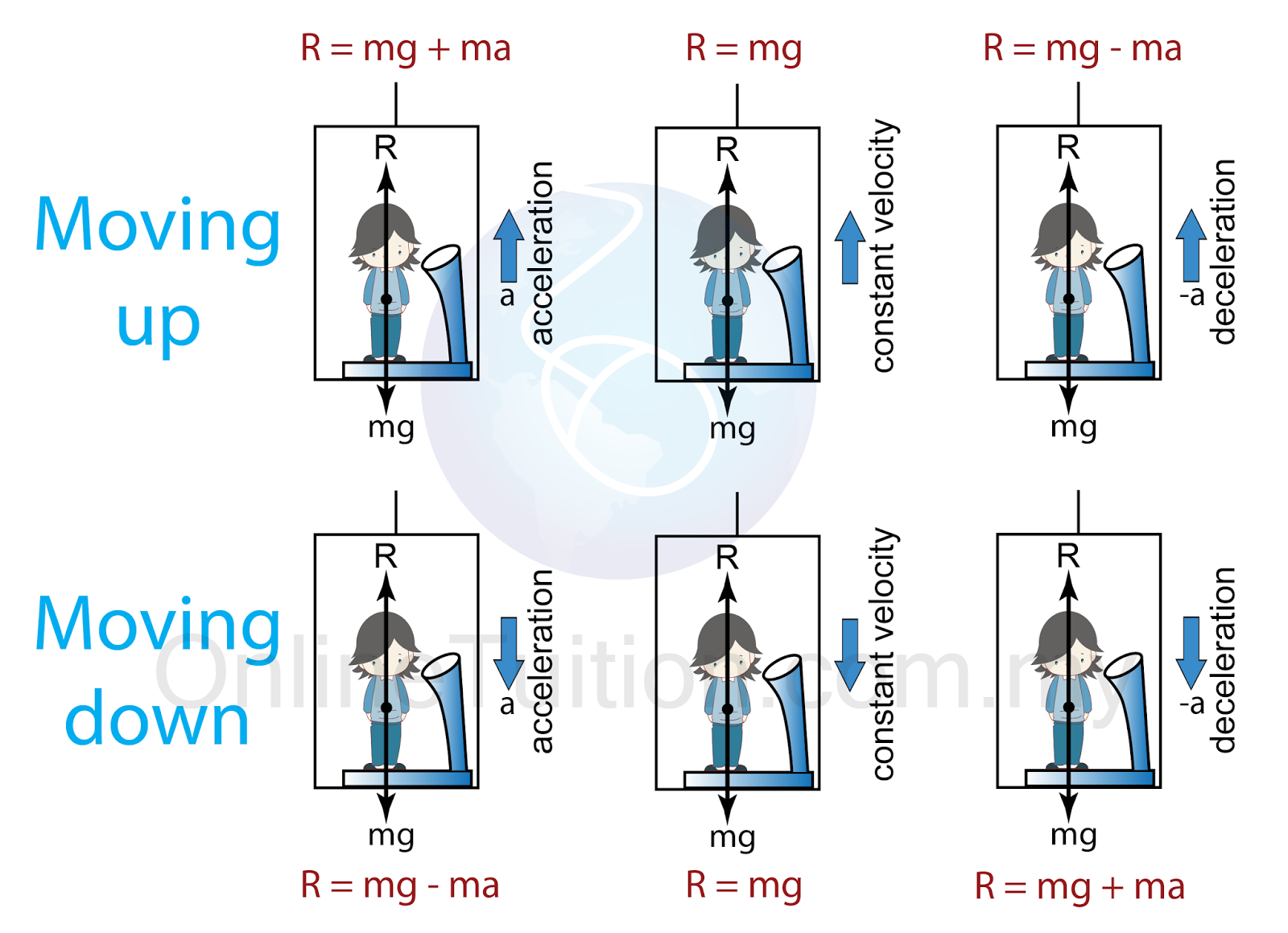
Case (a) If the lift moving with constant velocity v upwards or downwards. In this case, there is no accelerated motion hence no pseudo force experienced by observer $0^ {\prime}$ inside the lift. So apparent weight $\mathrm {W}^ {\prime}$ = Actual weight W. Case (b) If the lift is accelerated (i.e. a = constant upward) : Then net forces acting.

Physics Newtons 2nd Law Elevator Problem YouTube
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures!In this video I will give a short lecture on six different scenarios of what a person's ap.

McQuaid Physics Solving Elevator Problems with Newton's Second Law YouTube
k e Share 608 views 1 year ago Physics Unit on Forces This lesson addresses Physics problems, and also that feeling you've probably had when an elevator accelerates on an elevator ride,.

Physics Accelerating in an Elevator Example Problem YouTube
Elevator Problem. This is an application of Newton's second law to the forces felt in an elevator. If you are accelerating upward you feel heavier, and if you are accelerating downward you feel lighter.. For a mass m= kg, the elevator must support its weight = mg = Newtons to hold it up at rest. If the acceleration is a= m/s² then a net.

Newton's 2nd Law Accelerating Elevator. Level 1, Example 1 YouTube
According to Newton's second law, the forces acting on you are: ΣF = ma The overall acceleration is up, so the acceleration is positive. There are two forces in action, your weight down (-mg) and the supporting normal force. ΣF = N - mg N - mg = ma N = ma + mg N = m (a + g)

Numerical Problem Elevator Physics Problem Lecture 1 YouTube
4-5 The Elevator 1. An elevator is moving up at a constant velocity of 2.5 m/s, as illustrated in the diagram to the right: The man has a mass of 85 kg. a. Construct a force diagram showing the forces acing on the man. b. What force does the floor exert on the man? 2. The elevator now accelerates upward at 2.0 m/s2. a. Construct a force diagram.

Apparent Weight of an Object in a Lift SPM Physics
support force F = mass x acceleration + weight For a mass m= kg, the elevator must support its weight = mg = Newtons to hold it up at rest. If the acceleration is a= m/s² then a net force= Newtons is required to accelerate the mass. This requires a support force of F= Newtons.

Lift problem/Elevator problem laws of motion Unit3 Lecture9 Class 11RJ Physics classes
The force that accelerates the elevator comes from the cable of the elevator. And yes, Normal force is present but comes from the floor of the elevator which always exerts the same force of 98 N to balance the baby and prevent it from plummeting to the center of the earth; and this follows the Newton's third law.

How to Solve Elevator Problems in Physics (& AP Phys) Classes Apparent Weight and the Normal
Elevator Physics Imagine that you're in an elevator. the elevator has no acceleration (standing still or moving with constant velocity) the elevator has an upward acceleration (accelerating upward, or decelerating while on the way down) the elevator has a downward acceleration (accelerating down, or decelerating while on the way up)
Apparent Weight of an Object in a Lift SPM Physics
When the elevator goes up with an acceleration of magnitude a. When the elevator goes down with an acceleration of magnitude a. When the elevator is at rest. Solve the problem with respect to an observer at rest and later with respect to an observer who moves with the elevator. Ad blocker detected Knowledge is free, but servers are not.

Example Force Analysis Problem Solving Elevator Problem YouTube
Man In Elevator Problem Cole07 Nov 28, 2006 Elevator In summary, the force exerted by a 65-kg man on the floor of an elevator depends on the conditions of the elevator's motion. When the elevator is stationary, the man exerts a force of 637.65N. When the elevator accelerates upward at 2.3 m/s2, the man exerts a force of 787.15N.